What is IVF?
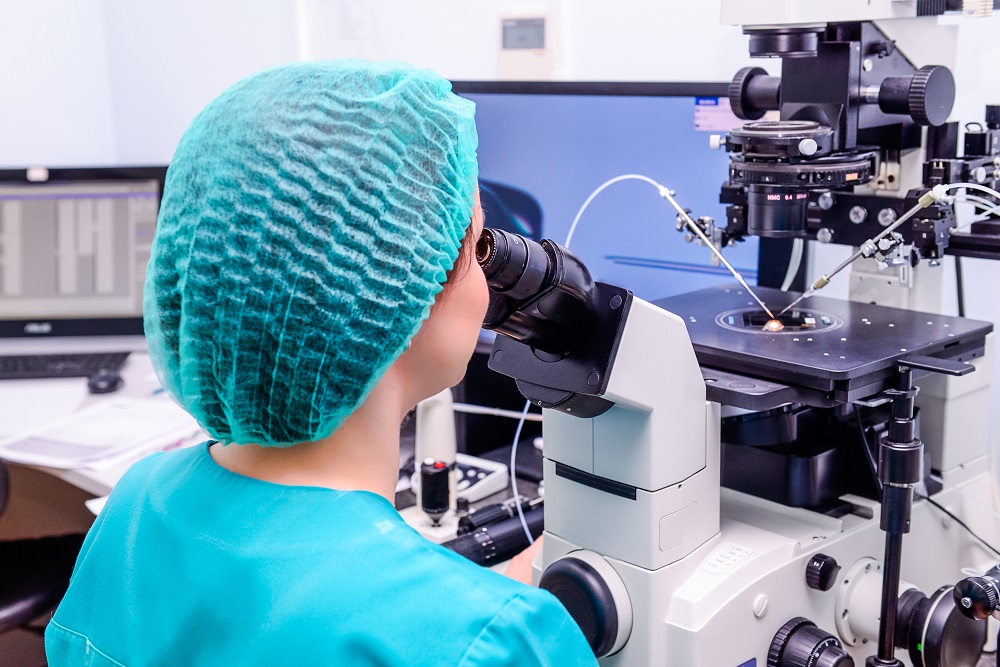
IVF is an abbreviated form of in-vitro fertilization which means sperm and egg (fertilize) meet up in the laboratory. We take out eggs from woman’s ovaries and make them fertilize with sperms in the IVF lab. This way embryos are formed some of which are transferred into the uterus while some can be kept frozen for future use.
When do you need to undergo IVF?
In women with blocked tubes, severe endometriosis, advanced age, poor ovarian reserve, low AMH and unexplained infertility, IVF process is a boon to achieve pregnancy. IVF is also needed for conception if the male partner has some problems like low sperm count, poor motility of sperms or morphologically abnormal sperms, etc.
Success Rates in IVF ?
Success rates after one IVF cycle vary from 40-80% depending upon the cause of infertility. Cumulative success rates after one fresh and one frozen transfer are quite high. The end result mostly depends upon the quality of embryos that we get after fertilization and lining of the uterus when we transfer those embryos. If we are transferring Day 5 embryos(Balstocysts) in a normal uterus with appropriate thickness & pattern of the uterine lining, the chances of a successful pregnancy are actually almost 80-90%.
Do we always have twins in IVF?
No, if we have A-grade blastocyst ( Day 5 embryo) then we can go ahead with single embryo transfer only. This way we are assured that we will have a singleton pregnancy. But mostly, we get twins in IVF as two embryos are transferred to increase the probability of successful pregnancy.
What is PGS?
Preimplantation Genetic Screening (PGS)
PGS is a genetic test done before embryo transfer (ET). For this, few cells are taken from an embryo (day 3 or day 5 i.e. Blastocyst) formed in an IVF Lab after fertilization. The removal of these cells has hardly any impact on the developing embryo, especially on Blastocyst (Day 5 embryo).
How is PGS done?
Cells from the embryo are removed through Laser-Assisted Biopsy by an embryologist. In a Day 5 Biopsy 4-8 Outer cells (which would form the placenta later) is taken and sent for chromosomal analysis. These cells are analyzed using the very efficient technique of Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) to determine the number of chromosomes in a cell.
How is PGS helpful ?
Normally 46 chromosomes are there in a healthy human cell, which is known as Euploid. Sometimes, there can be an abnormal number of chromosomes e.g. 47 or 45. Such a condition is known as an Aneuploid condition e.g. Down’s Syndrome, where there are 47 chromosomes in total due to three copies of Chromosome number 21. This can be the cause of failed IVF, miscarriage or even if pregnancy occurs, the child born will have mental and physical disabilities.
When do we need to do PGS?
To avoid such disappointment of recurrent IVF failure or miscarriage after successful IVF pregnancy, we have an option of PGS nowadays.
This test allows us to select a healthy embryo before planning embryo transfer.
Cost of IVF
The average IVF cost in Delhi for one cycle of IVF varies from 50k to 2.5 lacs depending upon the cause of infertility and the protocol followed. With PGS Though the cost of IVF cycle may escalate 20-30% But assurity of a healthy baby along with enhanced rates of Successful IVF cycle makes PGS quite a beneficial option.
When do we need to do IVF with PGS?
Its specifically important for people with repeated IVF failures, recurrent miscarriages, the advanced age of mother undergoing IVF and couples having a family history of genetic diseases.
How is the process of IVF done?
The whole process of IVF involved 8-10 days of injections followed by egg retrieval under anaesthesia. Fertilization in IVF lab using eggs and sperms through ICSI. When embryos develop into a blastocyst (Day 5 of fertilization), few cells are taken from the outer layer of the embryo by an expert embryologist. These cells are checked for a number of chromosomes in them. Embryos with an abnormal number of chromosomes, are discarded. Only the embryos with a correct number of chromosomes are used for transfer. It ensures the high success rate of the live birth of a healthy baby.